Troubleshooting Outlook: A Practical Guide for IT Support
When Outlook stops working as expected, users are quick to reach out—and often under pressure. Whether it’s slow performance, sync issues, or complete failure to launch, diagnosing Outlook problems requires a methodical approach.
This guide outlines essential steps to troubleshoot Outlook, from basic checks to deeper diagnostic tools, helping you determine whether the root cause lies with the client, the server, or in between.
Basic Checks#
Before diving into more advanced steps, start with a few quick validations:
✅ Restart the computer.
A full system reboot can clear temporary glitches, release locked resources, and restore network connectivity. This is often a quick fix and should always be your first step.✅ Is the internet connection working?
Confirm connectivity by opening a browser and visiting a few websites. Also check VPN status or proxy configurations if applicable.✅ Can the user access email via Outlook Web App (OWA)?
Log in through a browser. If OWA works fine, the issue is likely with the Outlook client. If not, investigate server-side or network issues. You can navigate to OWA (OutlookWebApp) through this link: https://outlook.office.com/mail/✅ Are the credentials correct?
Ask the user to log out and back in. Check for account lockout, password expiry, or recent changes to multi-factor authentication settings.
Outlook Won’t Start#
If Outlook fails to launch or crashes immediately:
Try Safe Mode Launch:
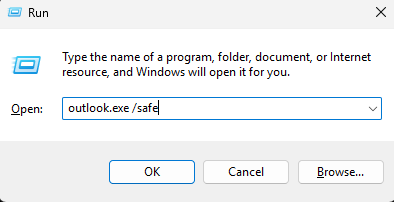 Open Run (
Open Run (Win + R), typeoutlook.exe /safe, and hit Enter. Safe Mode disables add-ins and loads only core functionality. If it launches successfully, suspect add-in issues.Review Event Viewer Logs:
Open Event Viewer and look underWindows Logs > Application. Filter by “Outlook” or “Office” to check for crash logs and faulting modules.Disable Add-ins:
In Outlook (if it opens), go toFile > Options > Add-ins.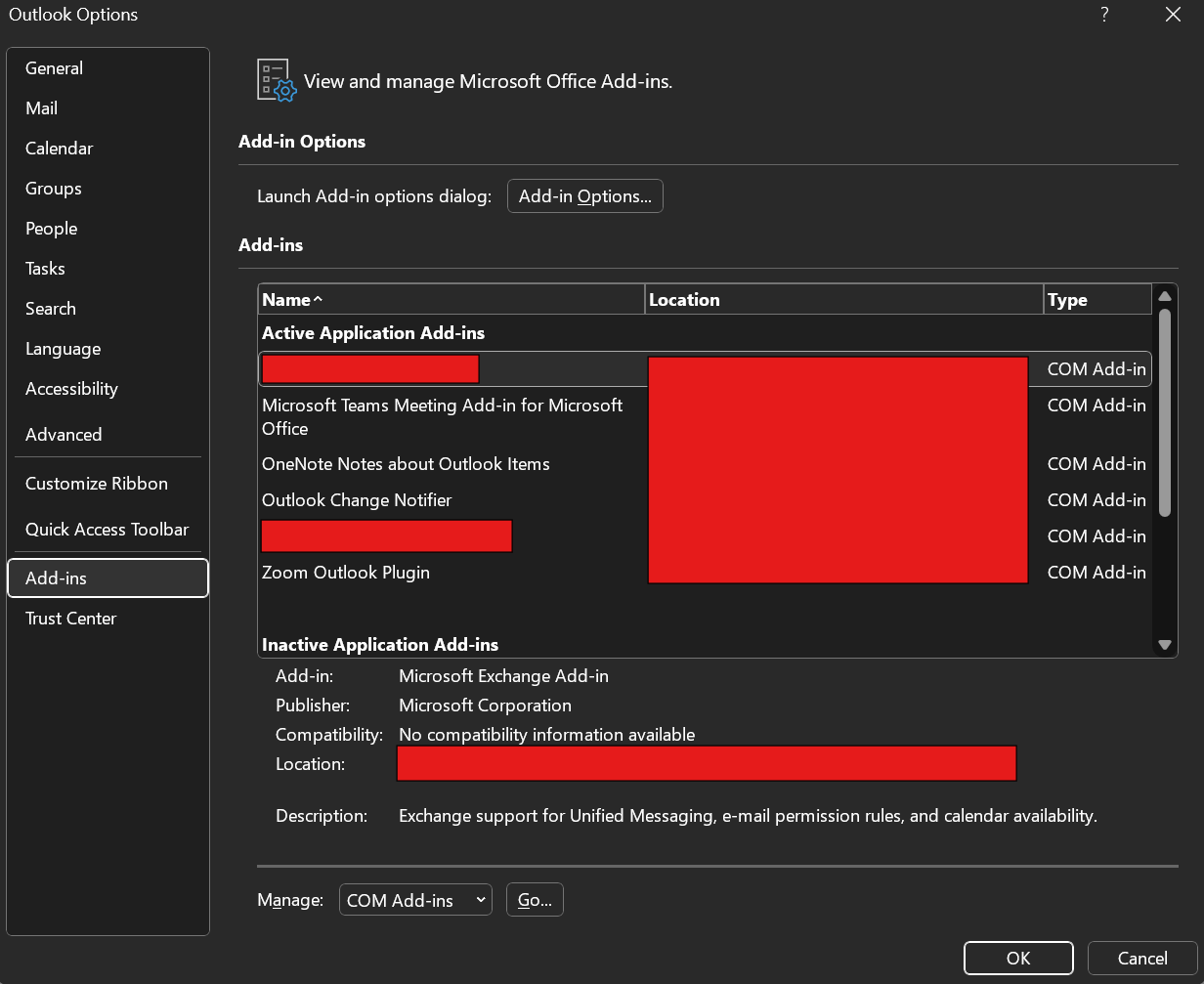 Then click
Then click Gounder COM Add-ins. Uncheck all non-Microsoft add-ins, restart Outlook, and enable them one by one.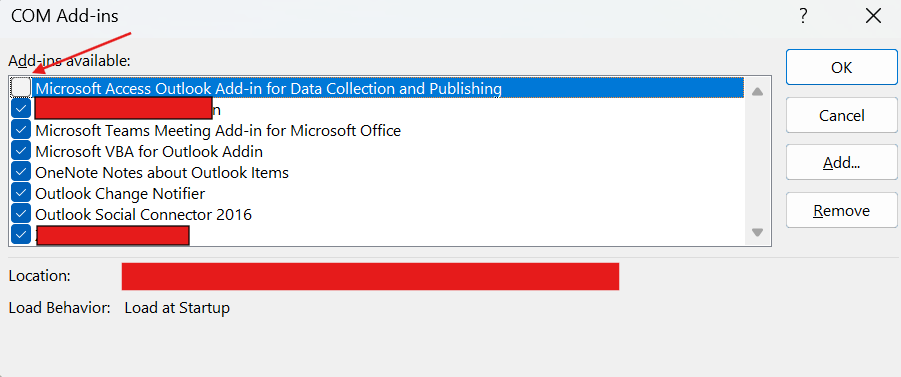
Recreate the Outlook Profile:
Go to Control Panel > Mail > Add.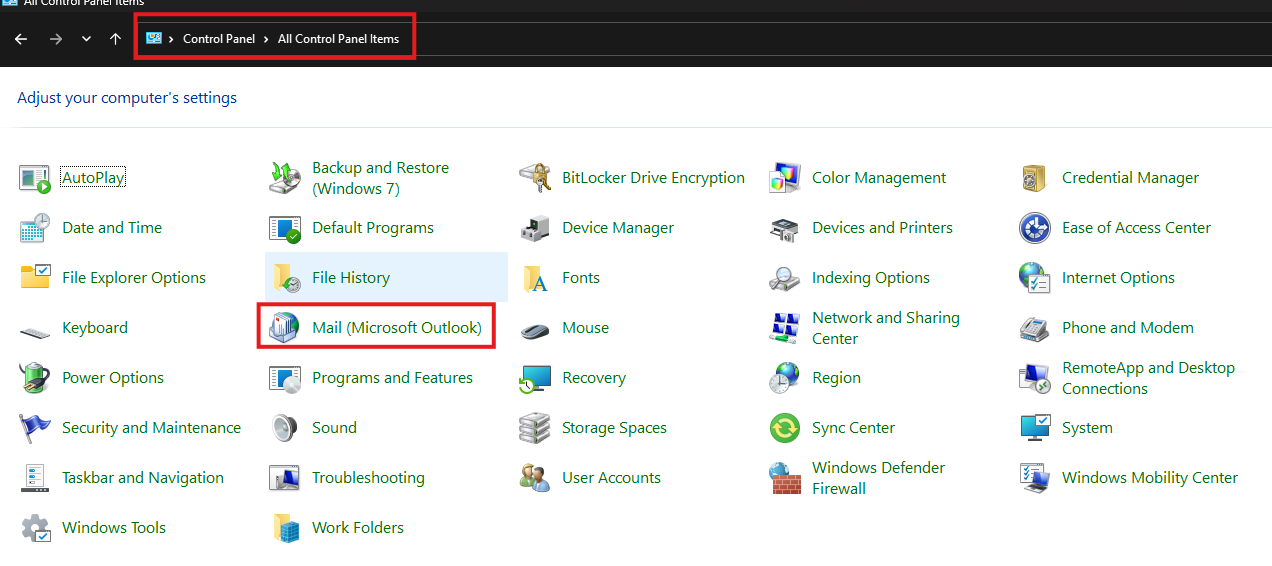
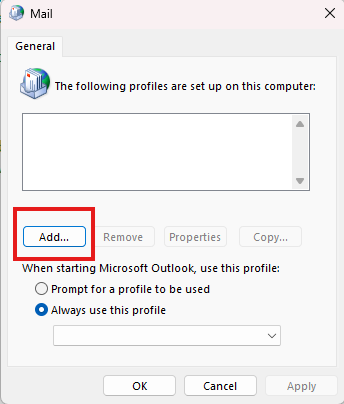
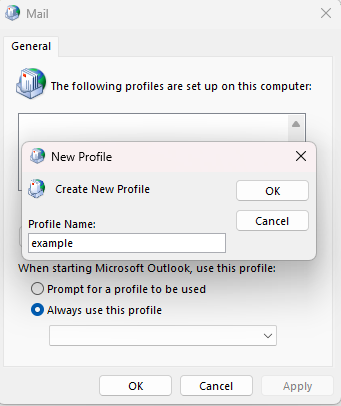
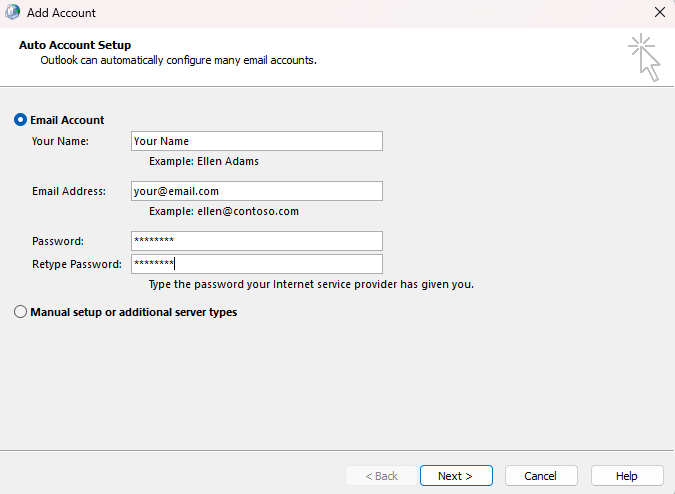
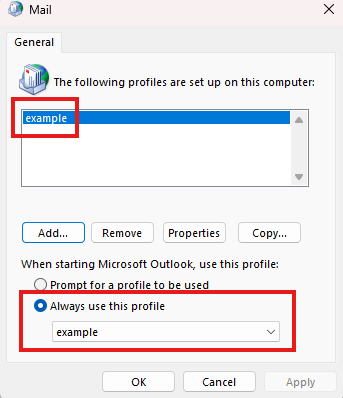
Create a new profile and configure the email account from scratch. Test with the new profile.
Check for Office Updates:
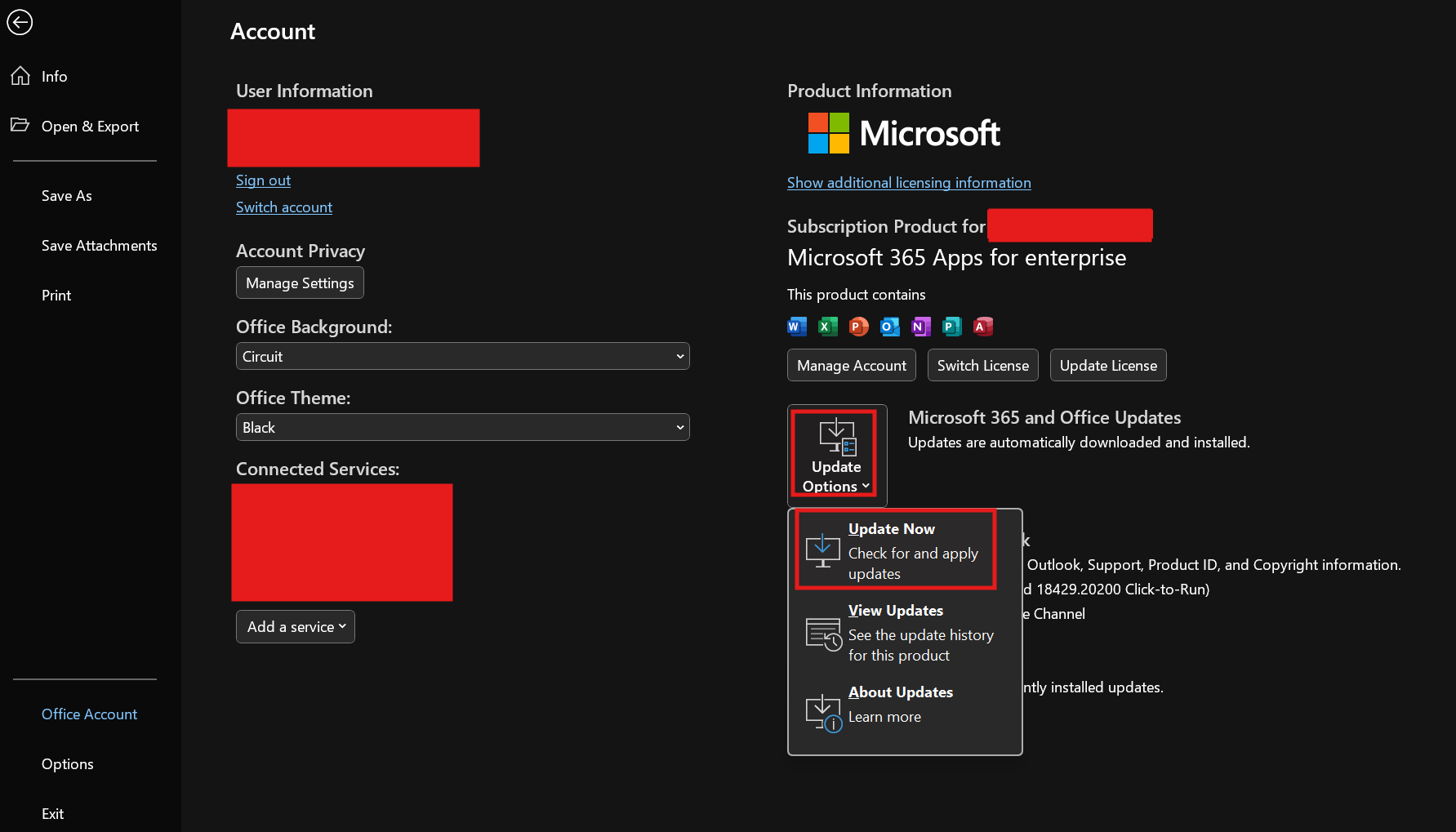 From Outlook, navigate to
From Outlook, navigate to File > Office Account > Update Options > Update Now. An outdated or broken update can affect launch.
Sync Issues#
If mail is missing or folders aren’t updating:
Check OWA:
If OWA shows all emails and folders correctly, the sync issue is local to the Outlook client.Confirm Connection Status:
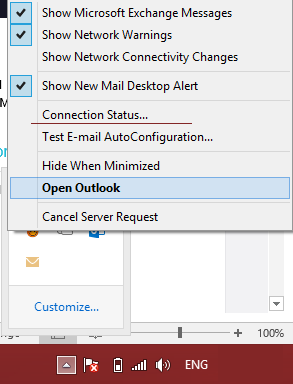 Hold
Hold Ctrland right-click the Outlook icon in the system tray. Click Connection Status and verify that all services are connected and authenticated.Use the Send/Receive Tab:
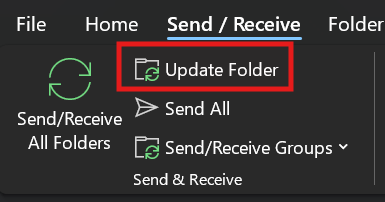 Manually trigger sync with
Manually trigger sync with Send/Receive > Update Folderor pressF9. Watch for sync errors at the bottom of the window.Check OST File Health:
Exit Outlook, go to the file location (usually in%localappdata%\Microsoft\Outlook), and delete the.ostfile. Outlook will recreate it upon restart.Enable Logging:
If problems persist, enable diagnostic logging withOutlook /log, then reproduce the issue and review the logs.
Common Errors and Fixes#
Outlook often throws numeric or vague errors. Here’s how to tackle some common ones:
0x800CCC0E – Cannot connect to the server:
Indicates server connection failure. Check SMTP/IMAP settings, firewall exceptions, and antivirus software.0x8004010F – Outlook data file cannot be accessed:
Typically due to a corrupt profile or inaccessible data path. Recreate the Outlook profile and check permissions on the Outlook data directory.Disconnected / Trying to connect:
Confirm that Outlook is online (check status bar). Verify credentials, and check DNS resolution and port availability usingTest-NetConnectionin PowerShell.
Diagnostic Tools#
When manual steps aren’t enough:
🛠 Microsoft Support and Recovery Assistant (SaRA):
A free tool from Microsoft that automates diagnosis and resolution of many Outlook issues. Download here🛠 ScanPST (Inbox Repair Tool):
For corrupted PST/OST files. Located in the Office installation directory. Run it and point to the data file path, then scan and repair.🛠 Outlook Logging Mode:
Launch Outlook with Run (windows key + R) and enterOutlook /logswitch to generate detailed logs under%temp%\Outlook Logging.
Add-ins and Third-party Plugins#
Outlook is highly extensible—but that can introduce instability.
Check Add-in Load Time:
In Outlook, go toFile > Options > Add-ins > Slow and Disabled Add-ins. Review which add-ins are affecting performance.Isolate Conflicts:
Disable all third-party add-ins, then re-enable them one at a time to identify which is causing the issue.Update or Remove Problematic Add-ins:
Especially antivirus email scanners or CRM integrations, which are common culprits.
Reset or Reinstall Outlook#
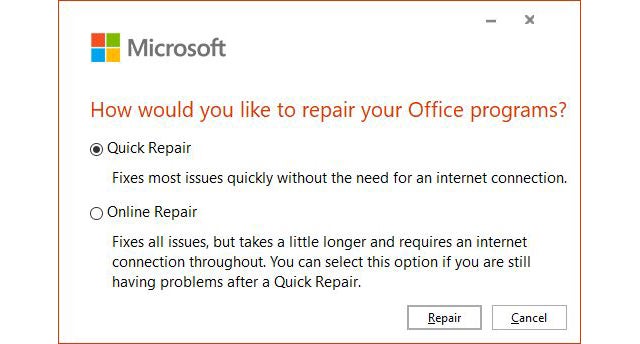
If all else fails:
Quick Repair:
Go to Control Panel > Programs > Microsoft Office > Change > Quick Repair. This preserves your settings and data.Online Repair:
A deeper reset that reinstalls all Office components. It removes settings but retains your data.Full Reinstall:
Uninstall Office, remove leftover files from%ProgramFiles%,%AppData%, and registry keys underHKCU\Software\Microsoft\Office. Then reinstall fresh.
Final Tips#
- Always test with OWA to quickly isolate local vs server-side issues.
- Document all steps, user complaints, and system logs for escalation or long-term analysis.
- Consider creating standard troubleshooting scripts or knowledge base articles to streamline support.