How to Troubleshoot SCCM Client Issues
What is SCCM?#
SCCM (System Center Configuration Manager), now part of Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager, is a systems management platform that enables IT administrators to manage large groups of Windows-based computers. It provides tools for:
- Software deployment
- Operating system imaging
- Patch management
- Inventory collection
- Remote control
SCCM relies on a local client agent installed on each managed machine. When the SCCM client fails, the device may stop receiving software updates, policies, or applications, and Software Center may not launch. This guide covers essential troubleshooting steps to restore client functionality.
Troubleshooting SCCM Client#
1. Restart the SCCM Client Service#
Sometimes the quickest fix is simply restarting the SMS Agent Host service:
Restart-Service -Name CcmExec -Force
After restarting the service, try launching Software Center manually:
Start-Process "C:\Windows\CCM\ClientUX\SoftwareCenter.exe"
2. Trigger SCCM Client Repair#
Use the built-in client repair tool to automatically fix corruption or misconfigurations:
Invoke-Expression "C:\Windows\CCM\ccmrepair.exe"
Or if the path isn’t known:
Start-Process -FilePath "ccmrepair.exe" -Wait -NoNewWindow
3. Re-evaluate Client Policies#
Sometimes SCCM policies become outdated or corrupt. Force a policy refresh using PowerShell:
Invoke-WmiMethod -Namespace "root\ccm" -Class "SMS_Client" -Name "RequestMachinePolicyNow"
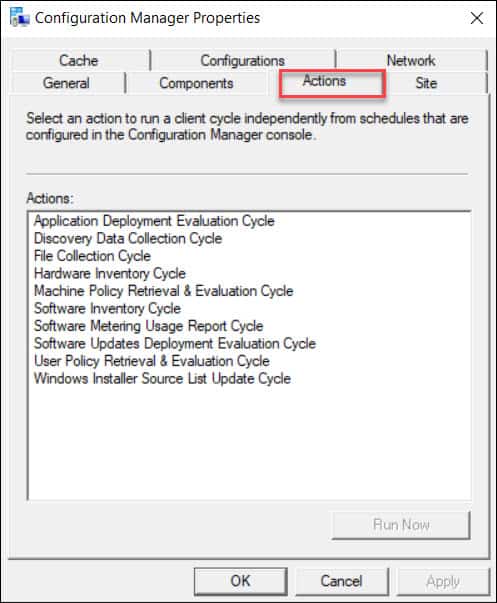
Alternatively, trigger the Machine Policy Retrieval & Evaluation Cycle:
$trigger = "{00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000021}"
Invoke-WmiMethod -Namespace root\ccm -Class SMS_Client -Name TriggerSchedule -ArgumentList $trigger
4. Validate Software Center Availability#
Check if the Software Center executable exists:
Test-Path "C:\Windows\CCM\ClientUX\SoftwareCenter.exe"
If it’s missing or won’t open, the client installation may be damaged.
5. Check Client Health from the SCCM Console#
Use the SCCM Console to view device status under Assets and Compliance > Devices and check:
- Client Health: Yes/No
- Client Activity: Active/Inactive
Note: Screenshot not available, describe or demonstrate live.
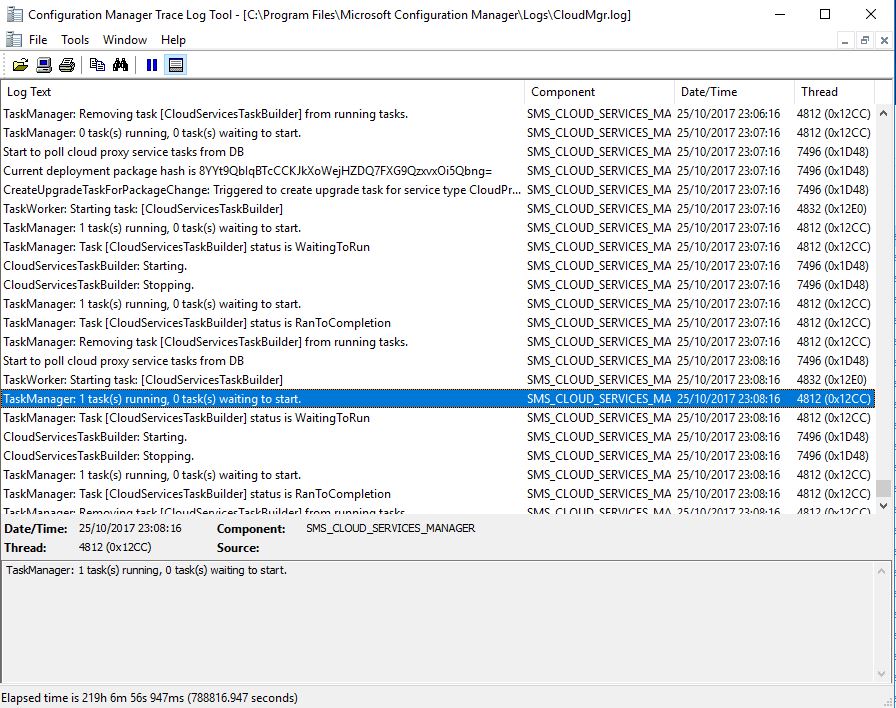
6. Review Client Logs#
Logs are stored in C:\Windows\CCM\Logs. Key logs to check:
ClientIDManagerStartup.log— client registration and ID assignmentccmexec.log— main client component operationsPolicyAgent.log— policy requests and evaluationsCAS.log,ContentTransferManager.log— content download issues
Use CMTrace.exe to view logs:
7. Reinstall the SCCM Client (Last Resort)#
If all else fails, uninstall and reinstall the client:
# Uninstall
C:\Windows\CCMSetup\CCMSetup.exe /uninstall
# Reinstall (replace SERVERNAME and SITECODE)
C:\Windows\CCMSetup\CCMSetup.exe /mp:SERVERNAME SMSSITECODE=ABC /logon
Example output:
C:\Windows\CCMSetup\ccmsetup.exe /uninstall
=> Starting client uninstall...
=> Client uninstall completed successfully.
C:\Windows\CCMSetup\ccmsetup.exe /mp:SERVER01 SMSSITECODE=ABC /logon
=> Starting client install...
=> ccmsetup.exe exited with return code 0
Final Notes#
Troubleshooting SCCM clients can be a time-consuming task, but following a structured approach helps isolate issues effectively. If problems persist, ensure the device has proper network connectivity, DNS resolution, and permissions to access the SCCM infrastructure.